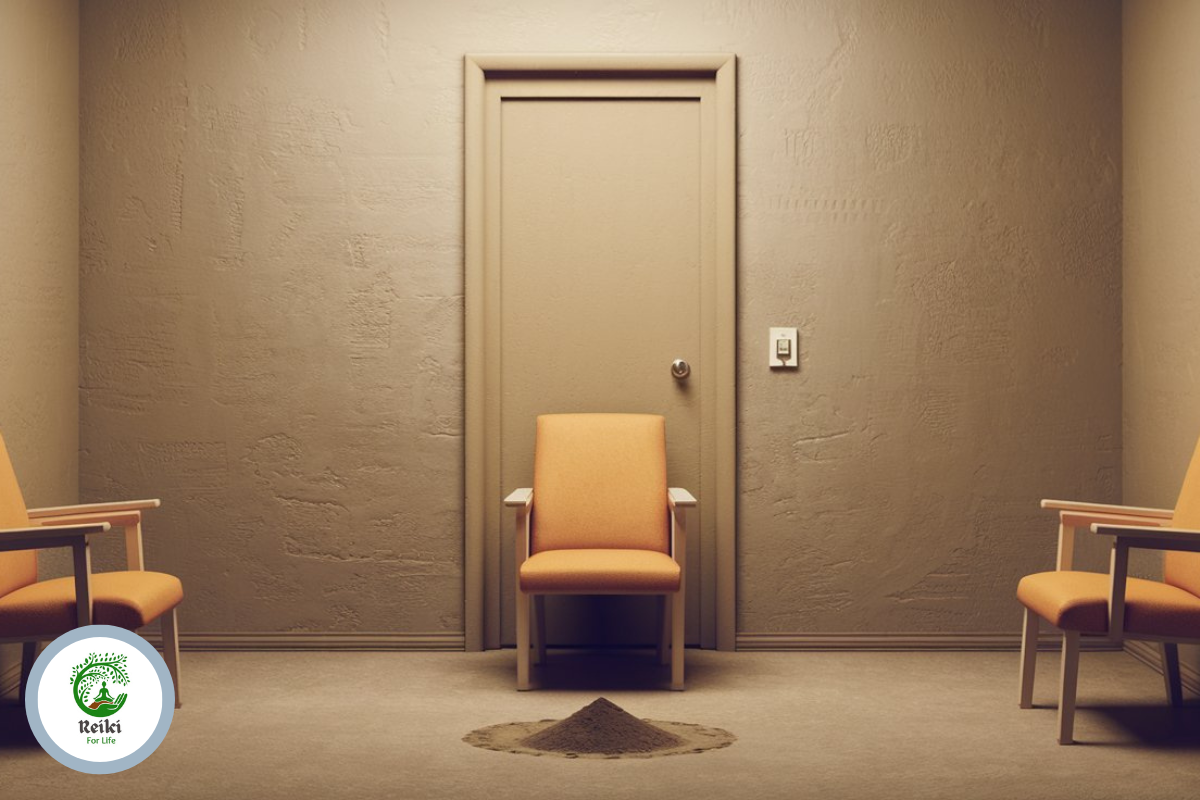
The illusion of choice affects our daily decisions without our knowledge. Whether it’s the fast-food menu or your streaming service, the options we think we have are often pre-selected, restricted, or limited by external influences. This clever psychological tactic has a big impact on marketing, politics, video games, and even everyday decision-making.
This post will explain what the illusion of choice is, how it operates, and provide instances from real life that might alter your perspective.
See Also: What Does It Mean to Be Emotionally Available?
What is the Illusion of Choice?
People experience the illusion of choice when presented with multiple options, but in reality, every choice they make leads to the same predetermined consequence. This concept is widely used in consumer psychology, social influence, and marketing. People are deceived into believing they have free will while, in fact, their choices are limited or controlled by an external entity, such as the government or a corporation.
Key Characteristics of the Illusion of Choice
- Controlled Options: The options are pre-selected or guided to achieve a particular result.
- Perception of Autonomy: People feel like they have control, but they don’t.
- Influence on Behavior: It influences decisions, making people feel more satisfied with their choices.
Famous Examples of Illusion of Choice
- Fast-food menus: Burgers, nuggets, and fries all seem to be options, but they are all made with the same ingredients (bread, meat, and potatoes).
- Supermarket Brands: Companies like PepsiCo, Unilever, or Nestlé frequently possess several “competing” items (like chips).
- Streaming Services: The pricing structure frequently encourages you to select the “middle” option when “Basic,” “Standard,” and “Premium” plans are available.
- Political Elections: Sometimes voters are given an option between multiple candidates, yet the policies of these candidates are often similar or influenced by the same groups.
How Do You Give Someone the Illusion of Choice?
One important strategy in sales, marketing, and negotiating is to provide the impression that there is a choice. Businesses, marketers, and even parents employ this psychological ploy in the following ways:
1. Limit the Options
Provide two or three options that all work toward the same end.
For instance, you could ask a child, “Do you want to do your homework before or after dinner?” rather than, “Do your homework.” Although the task (homework) is unavoidable, the child feels in charge.
2. Use the Decoy Effect
To encourage individuals to make a desired decision, include an unwanted option.
For instance, a streaming service for movies might provide three different price tiers:
- Basic: $10/month
- Standard: $20/month
- Premium: $22/month
Even though “Premium” wasn’t the original goal, the slight price difference between “Standard” and “Premium” makes it appear like the superior value.
3. Frame Choices with Anchoring
By using one option as a benchmark, you can make other options appear superior.
Example: Even if the $100 price was inflated, customers think they are getting a good deal when a store shows a “discounted” price of $50 next to the “original price” of $100.
4. Use Psychological Nudges
Display options in a way that “nudges” people toward their favorite.
Example: The “most popular” plan is frequently promoted when a customer signs up for a subscription. People are guided toward that option by this visual signal, which gives the impression that it is the “smart” one.
What is Another Word for Illusion of Choice?
The illusion of choice is also known as:
- False choice
- Pseudo-choice
- Controlled options
- Perceived autonomy
- Limited freedom
The illusion of control, which occurs when people think they have control over outcomes when they don’t, is strongly linked to the illusion of choice in psychology.
What is the Paradox of Choice?
The paradox of choice arises when people have too many options, which causes tension, worry, and indecision, but the illusion of choice deceives people into believing they have control.
Barry Schwartz, a psychologist, developed the paradox of choice, which holds that having too many options causes people to feel overwhelmed and less happy with their choice.
Illusion of Choice vs. Paradox of Choice
| Illusion of Choice | Paradox of Choice |
| Few, controlled options | Too many choices |
| Makes people feel in control | Leads to indecision |
| Used in marketing and sales | Observed in consumer behavior |
Examples of the Illusion of Choice
1. Supermarket Products
Though they are all owned by PepsiCo, you could believe you are choosing between Lay’s, Doritos, and Cheetos. There is no competition.
2. Streaming Services
A choice between Basic, Standard, and Premium plans might be presented to you. However, the “Standard” plan is frequently intended to be the most alluring choice.
3. Fast Food Menus
You can purchase wraps, burgers, or nuggets at fast-food restaurants, but they all employ the same basic components.
4. Elections and Politics
Although there are many candidates in elections, the policies of these candidates may be influenced by the same corporate donors, making the decision less significant than it first appears.
Illusion of Choice Quotes
Here are some popular quotes that capture the essence of the illusion of choice:
“You can have any color you want, as long as it’s black.” – Henry Ford (regarding the Model T car)
“Democracy is the illusion of choice between indistinguishable alternatives.” – Gore Vidal
“The greatest illusion of all is the illusion of control.” – Unknown
Illusion of Choice Memes
The idea of the illusion of choice has been elevated to a new level by memes. Here are some instances of memes related to this subject:
- Fast Food Meme: “Thinking you have 10 fast-food choices, but they’re all owned by 2 companies.”
- Streaming Meme: “Three streaming plans, but somehow you always pick the ‘Standard’ plan.”
These memes demonstrate how customers follow predetermined paths even when they believe they are making original decisions.
Conclusion
From the fast-food counter to the shopping aisle, from streaming subscriptions to political elections, there is an appearance of choice everywhere. It deceives individuals into thinking they are in charge, while in practice, businesses, governments, or systems restrict or control the options.
You’ll be more conscious of the influences on your choices if you comprehend the idea of the illusion of choice. Through marketing strategies, decoy options, or anchoring, you’ll be more prepared to make decisions on your own.
Give this article to someone who needs to understand how their “choices” are being manipulated if you found it helpful. Don’t let the illusion mislead you!
See Also: Reiki Palm Healing: Unlocking the Power of Energy Through Touch
FAQs
What is the illusion of choice?
When people think they have free options when, in fact, those decisions are predetermined or controlled by outside factors, this is known as the illusion of choice.
How do you give someone the illusion of choice?
By restricting options, employing the decoy effect, or employing nudges like anchoring, you can give someone the appearance of choice.
What is another word for illusion of choice?
The concepts of false choice, pseudo-choice, and perceived autonomy are other names for the illusion of choice.
What is the paradox of choice?
nxiety, hesitation, and discontent can result from having too many options, according to the paradox of choice.