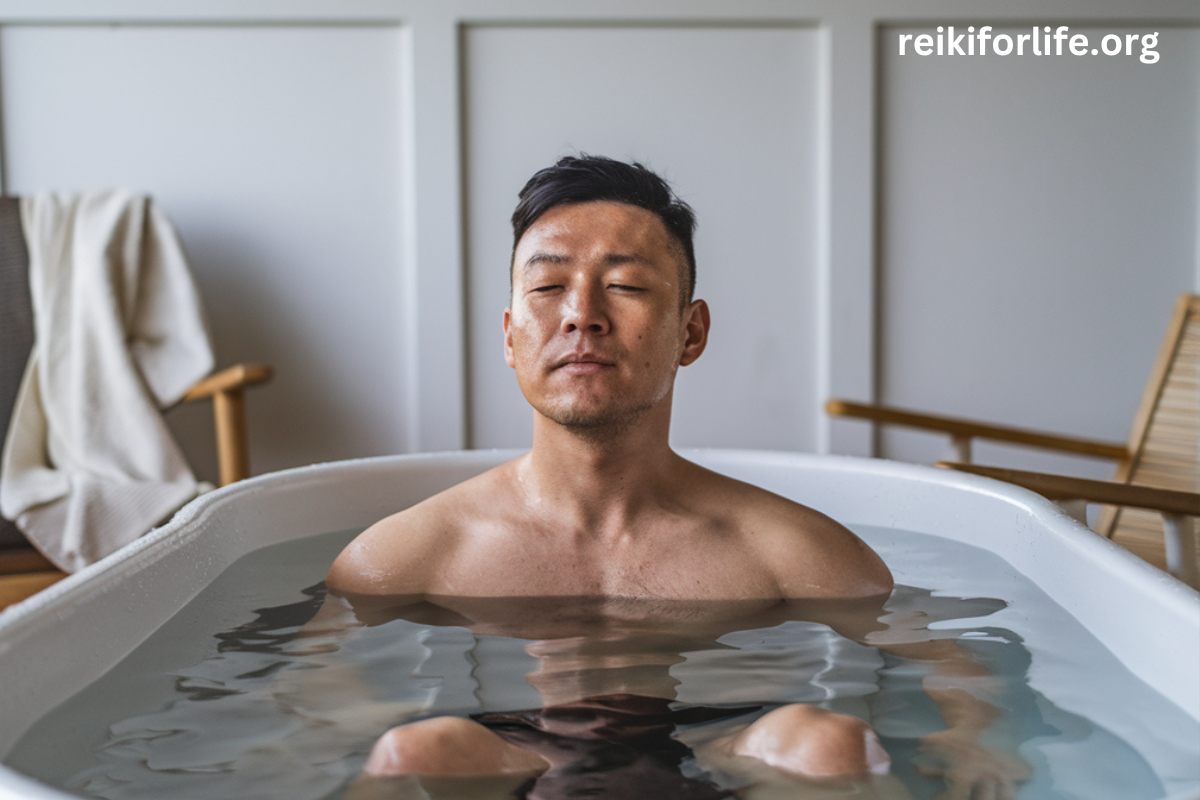
Cold water therapy has gained popularity as a natural way to boost health and aid recovery. From ancient civilizations to modern wellness trends, cold exposure has long been used for its healing properties. Whether through cold showers, ice baths, or cryotherapy, many people swear by its benefits. But while it offers some health advantages, it also carries potential risks that should not be overlooked.
The Health Benefits of Cold Water Therapy
- Improved Circulation
Cold exposure helps to constrict blood vessels, which can improve circulation and promote faster recovery. When the body warms up again, blood flow increases, delivering oxygen and nutrients to muscles and tissues, which is beneficial after exercise or injury. - Reduced Inflammation and Swelling
This is often used to reduce inflammation and swelling. Athletes commonly use ice baths to relieve soreness after intense workouts. By reducing blood flow to inflamed areas, cold water helps minimize swelling and alleviate discomfort. - Enhanced Immune Function
Research suggests that regular exposure to cold temperatures can help strengthen the immune system. Cold water stimulates the production of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections. Some studies show that cold water therapy can even reduce the frequency of colds. - Stress Relief and Mental Clarity
Cold water therapy is also known to have mental benefits. The shock of cold exposure can increase the production of endorphins, helping to improve mood and reduce stress. Over time, regular cold exposure is thought to improve resilience and mental clarity. - Improved Skin and Hair
Cold water can help tighten pores and improve the appearance of skin by reducing inflammation. It’s also believed to promote hair health by closing hair cuticles, which can make hair appear shinier and more resilient.
Why Cold Water Therapy May Not Be for Everyone
While cold water therapy has its perks, it’s important to understand that it isn’t suitable for everyone. There are several potential downsides to consider:
- Risk of Hypothermia
Prolonged exposure to cold water can lead to hypothermia, a condition where the body’s core temperature drops dangerously low. This is particularly a concern for individuals who aren’t used to cold exposure or for those who stay in the water too long. - Heart Health Risks
For individuals with heart conditions, sudden cold exposure can increase the risk of heart attack or arrhythmias. The shock of cold water causes a sudden constriction of blood vessels, which can strain the heart. People with pre-existing heart issues should consult a healthcare professional before engaging in cold water therapy. - Uncomfortable Experience
While some people embrace the shock of cold water, others may find it uncomfortable or even distressing. The initial exposure to cold can be overwhelming, leading to anxiety or panic in some individuals. This discomfort can deter many from using cold therapy regularly. - Limited Long-Term Benefits
While cold water therapy may provide immediate relief from soreness or inflammation, the long-term benefits are still debated. Some experts argue that excessive use of cold exposure may impair the body’s natural healing processes. It’s important to use cold therapy in moderation and as part of a well-rounded recovery plan. - Skin and Nerve Sensitivity
People with sensitive skin or conditions like Raynaud’s disease, which causes poor circulation in extremities, may experience negative side effects from cold water exposure. This can include numbness, tingling, or even frostbite in extreme cases.
Historic Use of Cold Water Therapy
Cold water therapy is not a modern fad—it has been used for centuries. Ancient Greeks, Romans, and Egyptians recognized the benefits of cold exposure for both physical and mental well-being. They used cold baths to treat injuries and promote overall health. In fact, the famous physician Hippocrates is known to have recommended cold baths to treat various ailments.
In the 19th century, this therapy was formalized as a medical treatment, with practitioners like Sebastian Kneipp, a German priest, pioneering hydrotherapy as a means to treat various diseases. Kneipp’s methods, which included immersing the body in cold water, were believed to improve circulation, boost immune function, and enhance overall vitality.
User Statistics and Trends
Recent surveys indicate that this style of therapy is becoming increasingly popular. According to a study by the National Institute of Wellness, 45% of regular users of cold therapy report feeling increased energy and improved recovery after physical exertion. Additionally, 60% of individuals practicing cold water therapy state they feel less stressed and more mentally clear after each session.
Interestingly, 35% of athletes use cold water therapy regularly for post-training recovery, citing significant reductions in muscle soreness and faster recovery times. On the other hand, 20% of participants have reported difficulty adapting to the cold and have chosen not to continue with the practice.
A Balanced Approach to Cold Water Therapy
From a health and healing perspective, this therapy can be beneficial when used correctly and in moderation. While it can help with inflammation, muscle recovery, and mental clarity, it is important to use it in conjunction with other wellness practices. It should not be relied upon as a sole method for recovery or overall health improvement. Always listen to your body, and if you have underlying health conditions, consult with a doctor before beginning any cold water therapy.
Conclusion
Cold water therapy offers numerous health benefits, including improved circulation, reduced inflammation, and enhanced immune function. However, it is not without risks. Hypothermia, heart health concerns, and discomfort are all potential downsides that must be considered. Historically, cold exposure has been used for centuries as a therapeutic method, but modern users should proceed with caution. If you decide to try cold water therapy, it’s best to start slowly, monitor your body’s response, and consult a healthcare provider if you have any concerns.